In recent years, the idea of 'Content Management System (CMS)' has become increasingly popular. This idea has gained traction in almost every industry. A Content Management System (CMS) is referred to as software or a system for managing, storing, and distributing content for an organization. It can be used by companies of all sizes and types. The application provides increased efficiency, versatility, content control, and improved team collaboration. But the secret to making the most of a CMS platform relies on choosing the right one. So, being familiar with the different kinds of content management systems can assist you in opting for the right one for your business.
Although the term is often unclear over the years, these are the five most popular Content Management Systems (CMSs) that can help you manage digital content. Let's understand in detail along with its advantages, and examples. In case you are looking for a head start on understanding the CMS used in the ecommerce industry, you can explore one such best ecommerce CMS CatalogsBuilder here.
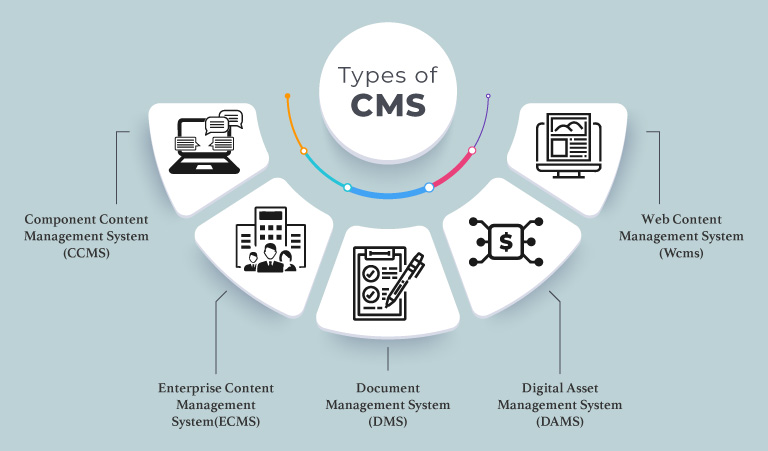
Types of Content Management Systems (CMS)
1. Component Content Management System (CCMS)
CCMS is a Content Management System specializing in handling content on a granular level. Instead of managing content page by page, it stores words, phrases, paragraphs, and photos (termed "components") in a centralized database.
Every single item of content is considered a single entity and is stored in the system by CCMS. Through its trusted content management system, the CCMS publishes content across mobile, PDF, and print platforms.
Advantages of CCMS:
Reusability: This method of reusing content saves time while editing and writing content.
Transparency: Users cannot dispute its total content transparency as it is irrefutable.
Traceability: Since the content is handled at a granular level, each detail of the page or document can be tracked.
Omnichannel Publishing: CCMs allows content to be distributed across multiple channels, such as the web, chatbots, mobile apps, and print.
Enhanced Team Collaboration: By improving workflow, the CCMS helps non-technical and technical teams collaborate efficiently.
Examples of Component Content Management systems (CCMS) are Vasont, XDocs, SDL Live Content, Paligo, Documentum, Author-It, Xyleme, etc.
2. Enterprise Content Management System (ECMS)
An Enterprise Content Management System (ECMS) utilizes various tools and techniques such as scanning, tracking, indexing, and so on that help manage information. However, an organization's documentation is collected, organized, and delivered, using these strategies to ensure vital information reaches the right people.
The content of an ECMS determines a company's core framework. These large-scale software packages make it easy to generate reports for tracking and controlling their complex operations.
Having an ECM makes it easy for a business to gain access to the information they need for project completion and effective decision-making. One of the benefits of ECMS is that after using the required content, the files will get deleted automatically after a specified period. The process prevents the storage of useless data.
Advantages of ECMS:
More Flexible: ECMs are capable of capturing any file type, from any location, along with automating its storage and processing.
Enhanced Efficiency: With documentation taken care of, you can be more productive in creating content and your daily tasks.
Efficacious: Enterprise Content Management reduces costs by storing only the necessary files and deleting the rest.
Examples of Enterprise Content Management systems (ECMS) are Atlassian, Confluence, Zoho Docs, eFileCabinet, DocuShare, and Box.
3. Document Management System (DMS)
The use of paper is almost extinct. Paper-based business records were the thing of the ancient era. Today, we have DMSs. A Document Management System (DMS) allows users to manage virtual documents that are stored in the cloud. Cloud storage, however, can perform functions such as managing and tracking documents. Using a DMS, websites or company documents can be organized, secured, digitized, and classified with ease. DMSs also offer high security to ensure that content is confidential.
Advantages of DMS:
Eco-Friendly: Organize and store content digitally and save paper at the same time!
Security: DMSs are designed to keep sensitive information secure in safe hands by offering multi-level security.
Remote Access: It allows you to access and edit your documents remotely (mobile access) from any location.
Examples of Document Management Systems (DMS) are Google Workspace, Dropbox, OneDrive, ClickUp, HubSpot, and iCloud.
4. Digital Asset Management System (DAMS)
Digital Asset Management System is a technology that manages digital assets and business processes. With a Digital Asset Management System (DAMS), it becomes much easier for users to organize, share, and store digital assets. Audio, creative files, video, documents, and presentations are among these assets. It is a cloud-based Content Management System (CMS) that simplifies the management of digitized documents.
DAMS includes several types, namely Product Asset Management Systems, Digital Supply Chains, Library Asset Management Systems, and Brand Asset Management Systems. The varying purpose of each of these DAMSs contributes to managing the overall digital content.
Advantages of DAMS:
Centralized Library: DAMS stores its content in a centralized repository, which allows it to be accessed by multiple users easily.
Managing Brands Effectively: A DAM allows users to access important files through a branded web portal.
Publishing Digital Content: A DAM lets you publish digital content to third-party distribution services, social media channels, and more.
Examples of Digital Asset Management Systems (DAMS) are Brainfolder, Bynder, Canto, Cloudinary, Bynder, and MediaValet.
5. Web Content Management System (WCMS)
Web Content Management Systems (WCMS) are specialized CMS solutions designed exclusively for websites and it only deals with web content. Users of a web content management system can manage and edit website content without knowing how to code or markup. To manage digital content, WCMSs provide collaboration, authoring, and administration tools.
Advantages of WCMS:
Personalization: WCMSs allows users to create personalized web pages based on their personal preferences.
Automation: With WCMS, publishing is automated, which improves workflow management and reduces workload.
Scalable: WCMSs offer the ability for enterprises to grow rapidly without exceeding the limits of their website.
Examples of Web Content Management Systems (WCMS) are Hubspot, Drupal, WordPress, Webflow, and Duda.
There are a few other types of content management systems besides these five that can be considered subcategories of main CMSs. These are categorized by how they are integrated into your system. Examples include:
Open-Source CMS
Proprietary CMS
Cloud-Based (SaaS) CMS
Headless CMS
Custom CMS
A comparison of similarities and differences:
Each Content Management System serves a different purpose. CMSs are all built with a similar objective under this heading: to make it easier for users to retrieve and understand the content. Because of this, all Content Management Systems feature similar functions at their core. Here are a few of them:
Easy storage of digital content.
Content accessibility like fetching, searching, editing, and modifying content.
Automatic version control of published content.
Detailed reporting after analyzing content.
Streamlined delivery of content.
Pre-designed layouts and templates.
There is more or less the same objective for all Content Management Systems, but the features differ significantly. The objectives of every CMS are different, and they each serve different purposes when viewed from a strategic standpoint. CCMS retrieves and stores the content in its entirety, while WCMS manages the website layout. Product asset management and supply chain management are taken care of by DAMS, while ECMS manages company-wide information. However, DMS and MCMS rely on cloud storage to streamline content management.
Conclusion:
Content Management Systems (CMS) facilitate the management of content at several levels. Since there are so many options for content management tools available in the market, choosing the right one can be a challenge. It's wise to examine all types of content management systems before choosing one.To choose the right tool, one must have a deep understanding of what it does and what purpose it serves. By thoroughly researching and analyzing each Content Management System, the work becomes more straightforward and less risky. Now a days online store owners are adopting to new CMS tool that helps them to manage product information across different channels in consistent manner and helps them to increase sales conversion. A popular and widely used ecommerce CMS can be referred here, Modern day product catalog management and in case you need any help the team can be contacted here.







Chirayu
How can a thorough understanding of different types of content management systems aid in choosing the right one for a business?